
Air conditioners (also referred to as AC) provide thermal and humidity management in spaces, such as industrial facilities and data centers, where temperature and humidity control is necessary. They can be used to supplement HVAC systems, supplying spot or space cooling if existing HVAC is inadequate, or to provide air temperature and humidity control where HVAC is unavailable.
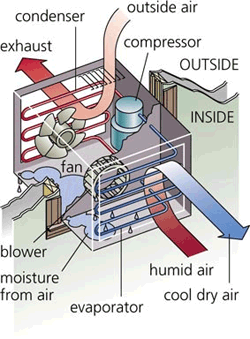
Air conditioners chill air by passing indoor air over evaporator coils, returning the chilled air to the room and exhausting the heat removed to the outside.
The components of an air conditioner include:
In addition to the familiar window-mounted air conditioners, several newer options are well-suited to spaces where a window unit is not feasible.
Ceiling-mount unitsare available in both suspended and flush-mount configurations. This configuration is particularly useful in computer rooms or other spaces where spot cooling is needed.
Ductless, split unit, and mini-split unitair conditioners are used in spaces that lack ductwork for HVAC systems. With split-unit systems, different rooms can have separate controls. The compressor is outside the space, reducing ambient noise.
Enclosure unitsare designed specifically for cooling enclosures that contain electronic equipment. Find additional information about enclosure air conditioners here.
Portable air conditionersare built with wheels, allowing the user to move as needed. Intake and exhaust hoses must be placed outside a window, limiting this type of air conditioner's use to spaces with a window.
All air conditioners share basic specifications, regardless of physical form.
Cooling capacity (kilowatts, tons, or BTU/hour): Manufacturers generally provide sizing software and/or services to assist in determining cooling loads
Electrical specifications:
NEMA standard electrical equipment enclosure type: For information on NEMA enclosures, see the Standards link below.
Refrigerant type: For more information about refrigerant types, follow this link.
Control systems:Temperature and humidity controls and thermostats range from simple switches and settings to sophisticated programmable units. Additional information about thermostats and thermal switches is available here .
Some applications require additional features: